Introduction to lithium-ion batteries, one of the most popular rechargeable batteries today
- August 28, 2023
- Venier

Lithium-ion batteries are one of the most popular rechargeable batteries today, and they are widely used in digital products, power tools and electric vehicles. This kind of battery achieves charge and release by embedding and removing lithium ions, and has the advantages of small size, light weight, fast charging, long service life and environmental protection.
Compared with traditional nickel-cadmium batteries, lithium-ion batteries have a high recovery rate, do not contain heavy metals, and emit very few pollutants, which can effectively reduce the impact of batteries on the environment. At the same time, the high energy density of lithium-ion batteries makes them have very good high temperature performance and low temperature performance, and can work stably in various environments.
1. Introduction to lithium-ion batteries
A lithium-ion battery is a type of secondary battery (rechargeable battery) that primarily relies on lithium ions moving between the positive and negative electrodes to work.
In the process of charging and discharging, Li+ is embedded and deembedded between the two electrodes. When charging, Li+ is deembedded from the positive electrode and embedded into the negative electrode through the electrolyte, and the negative electrode is in a negative lithium state. The opposite is true for electrical discharge.
Lithium-ion battery voltage range 2.8V~4.2V, typical voltage 3.7V, lower than 2.8V or higher than 4.2V, the battery will have the risk of damage.
2. Concepts of 1C and 0.1C
The unit of battery capacity is mAh, C refers to the rate of battery charging and discharging, such as a 2000mAh battery, 1C discharge refers to the size of the discharge current is 2000mA, 0.1C is 200mA, charging is the same.
3. Advantages and disadvantages of lithium-ion batteries
The main advantages of lithium-ion batteries:
• Lithium-ion batteries have high voltage and high energy density;
• Long cycle life, generally can cycle 500, or even more than 1000 times;
• Self-discharge is small, and the self-discharge rate of Li-ion fully charged at room temperature after storage for 1 month is about 10%;
• Fast charging, 1C charging capacity can reach 80% of the nominal;
• Wide operating temperature range, generally -25~45°C, which is expected to break through -40-70°C;
There is no memory effect like Ni-Cd and Ni-Mh, and the remaining power is not used up before charging;
• Compared with Ni-Cd and Ni-Mh, it is environmentally friendly and pollution-free (no cadmium, mercury and other heavy metals);
The main disadvantages of lithium-ion batteries:
• High cost;
• Need to protect the circuit board, including overcharge and overdischarge protection;
• Can not be large current discharge, the general discharge current is below 0.5C, too large current leads to internal heat of the battery;
• Poor safety, easy to explode, fire.
4. The difference between lithium batteries and lithium-ion batteries
Lithium battery and lithium-ion battery are two different concepts, the main differences are as follows:
The positive electrode material of lithium battery is manganese dioxide or thionyl chloride, and the negative electrode is lithium;
Lithium-ion battery is a lithium battery containing lithium compounds as a positive electrode, in the charge and discharge process, no metal lithium exists, only lithium ions; Lithium battery is also known as a lithium battery, can be continuous discharge, can also be intermittent discharge, once the power is exhausted can not be used again, can not be charged;
Lithium-ion batteries, also known as secondary lithium batteries, can be charged and discharged;
5. Lithium-ion battery charging mode
The ideal charging mode for lithium-ion batteries is called CCCV mode, that is, constant current and constant voltage mode.
In the figure below, gray is the battery voltage, green is the charging current, and red is the battery capacity.
When the battery voltage is low, the battery is charged with a fixed constant current. When the battery voltage reaches 4.2V, the constant current mode will be switched to constant voltage mode. Since the battery voltage is not allowed to exceed 4.2V, the system gradually reduces the charging current until it approaches 0. When the battery voltage is 4.2V and the charging current is 0, the battery is fully charged.
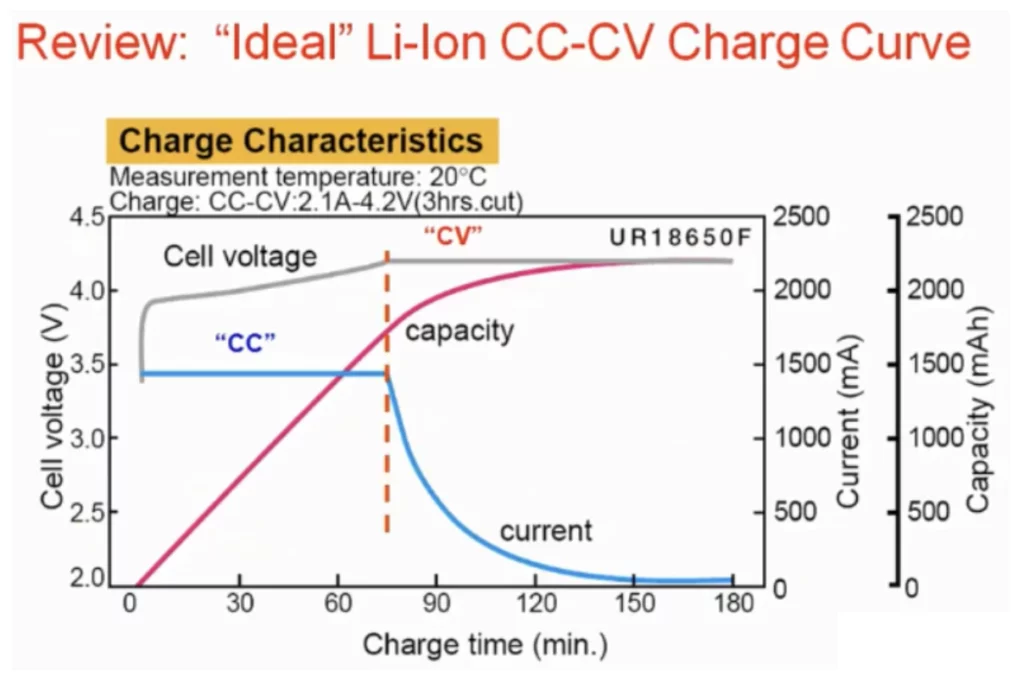
Lithium ion battery CCCV mode
In order to ensure the absolute safety of the battery, the actual charging mode will be more refined, and charging according to constant current for uncertain batteries will cause greater damage to the battery. Test mode, when the battery voltage is lower than 2V, it will wake up the battery with a small current; Trickle charging, also known as precharge mode, when the battery voltage is between 2V and 3V, it will be precharged with 1/10 or 1/20 of the constant current charging; Constant current charging: When the battery voltage rises to more than 3V, the battery will be quickly charged in constant current mode; Constant voltage charging: When the battery voltage reaches 4.2V, the battery will be charged in constant voltage mode;
Like TI’s scheme, when the battery voltage is 4.2V and the charging current is low but not 0, about 1/10 of the constant current charging current, the charging will stop, and the battery voltage will be reduced to 4.16V or 4.17V.
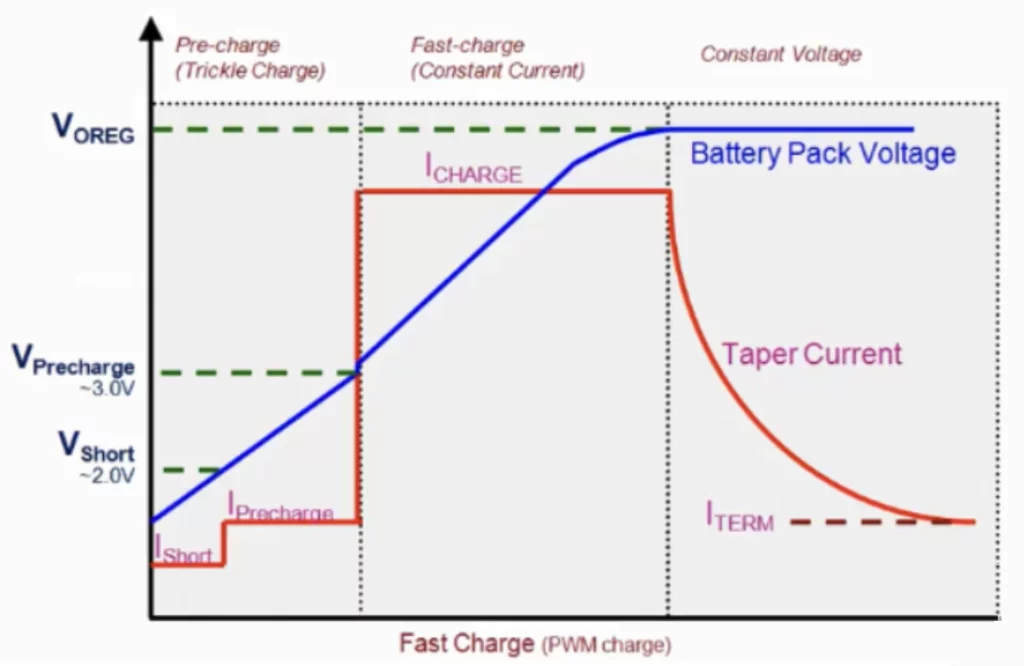
The three stages of charging a lithium-ion battery
6. Why is the charging cutoff voltage of lithium-ion battery 4.2V
The following is the relationship between the cycle life of the battery and the charge cut-off voltage, in the initial cycle of the battery, charging to a slightly higher voltage will get a higher single-cycle charge, but only for a short period of time.
When the charging voltage of the battery is 50mV or 100mV higher than the recommended maximum voltage of 4.2V, the aging speed of the battery will be greatly accelerated due to slightly overcharging each cycle. In summary, the charging cut-off voltage of the battery is higher than 4.2V, the higher the voltage, the shorter the cycle life, and the faster the battery capacity decline.
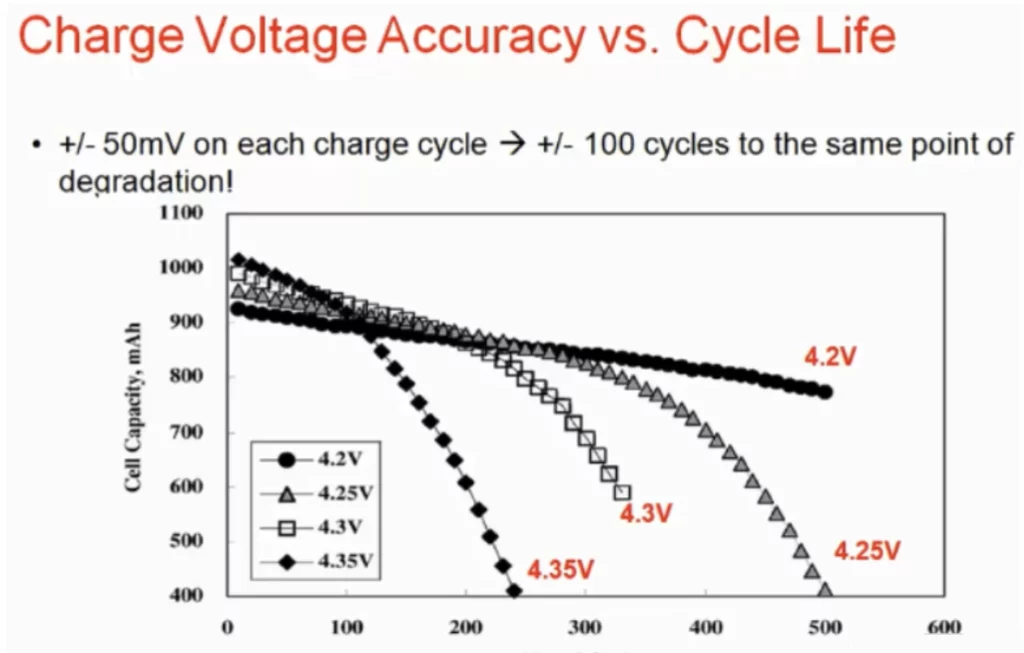
Relationship between cycle life of lithium ion battery and battery charging cut-off voltage
7. Lithium ion battery discharge curve
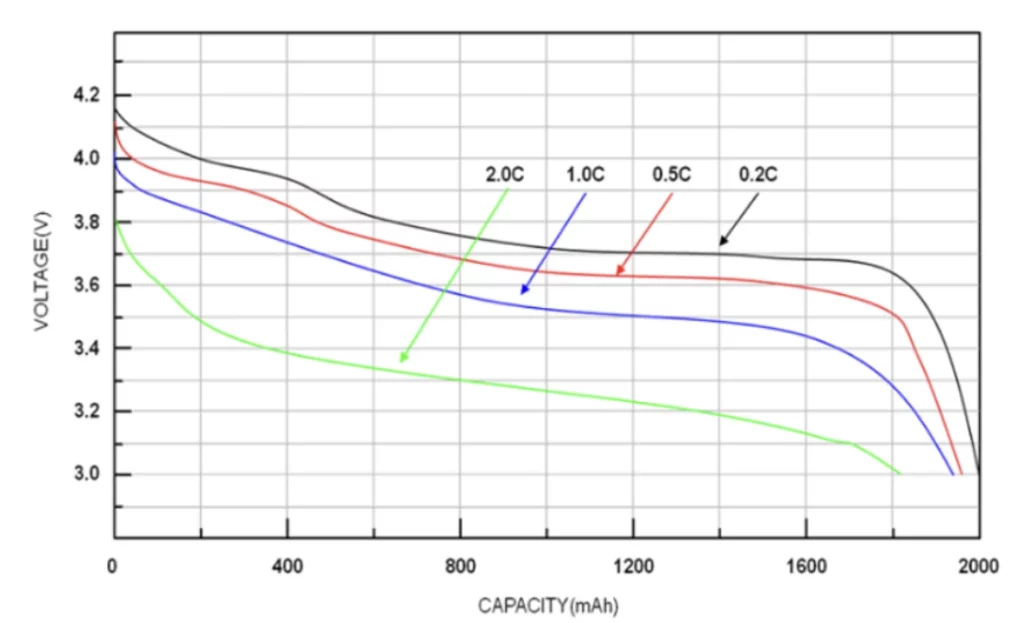
The following is the discharge curve of the lithium-ion battery at different discharge currents, it can be seen that the greater the discharge current, the faster the capacity of the battery decreases, the lower the capacity, and the more insufficient the nominal capacity of the battery is used. When the battery capacity is lower, the internal resistance of the battery will increase more, and when the current is discharged, the internal resistance grows faster.
Discharge curves of Li-ion batteries at different temperatures.
It can be seen from the battery discharge curve at different temperatures that the lower the temperature, the faster the battery capacity decreases and the more inadequate the discharge. The temperature of the battery is below 0 degrees, the internal active ingredients are very weak, and the internal resistance will increase accordingly; Excessive temperatures can also damage batteries.
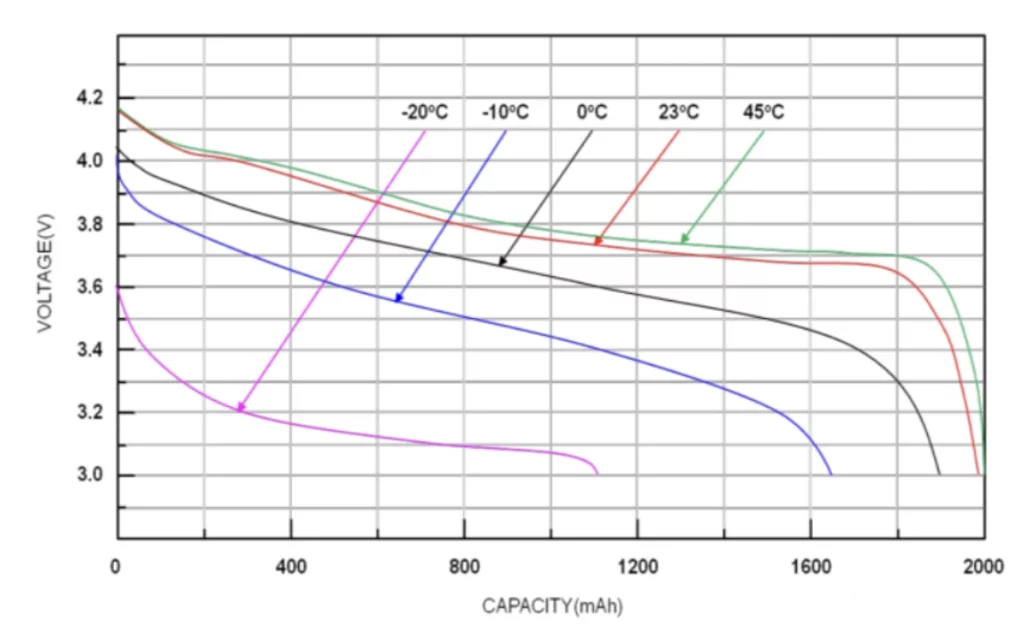
Discharge curve of lithium ion battery at different discharge current
8. Number of lithium-ion battery cycles
In practice, whenever the accumulated discharge capacity is equal to the design capacity, it is recorded as a cycle.
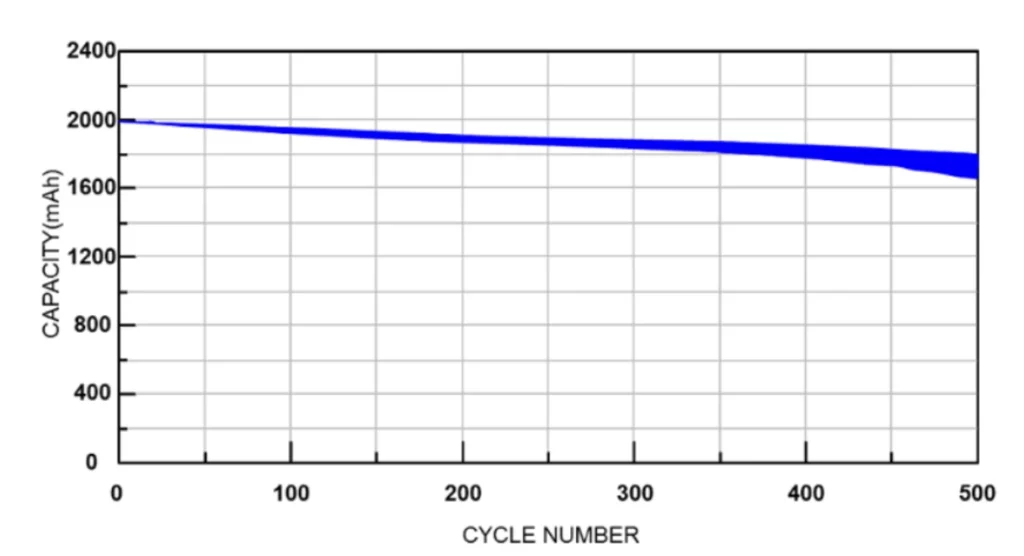
Lithium-ion battery cycle life
The national standard stipulates the test conditions and requirements for the cycle life of lithium-ion batteries: charge at 1C for 150 minutes at 25 degrees room temperature, and discharge current at constant current 1C to 2.75V for a cycle. When one discharge time is less than 36 minutes, the test ends, and the number of cycles must be greater than 300 times. This definition specifies that the cycle life test is carried out in a deep charge and deep discharge manner; The cycle life must be more than 300 times after the execution of this mode, and the capacity is still more than 60%;
9. Li-ion battery operating voltage range
The operating voltage of lithium-ion batteries has a range, and different cell manufacturers will vary, but the difference is not large.
Related Posts

The United States plans to build a complete lithium battery industry chain in the country: from mining to recycling
The new goal for the United States is to engage in all aspects of lithium-ion battery production, from mining to manufacturing, and ultimately recycling, within its borders by 2030. Failure to do so could jeopardize the country’s climate goals and its ability to compete in the rapidly growing electric vehicle industry.

An In-depth Guide to Doorbell Types, Battery Replacement, and Choosing the Right Lithium Battery
Doorbells have come a long way since their invention, from simple mechanical time tellers to high-tech wireless devices that offer a variety of functions. We’ll explore the different types of doorbells, the basic considerations when replacing batteries, and how to choose the right lithium battery for your doorbell.